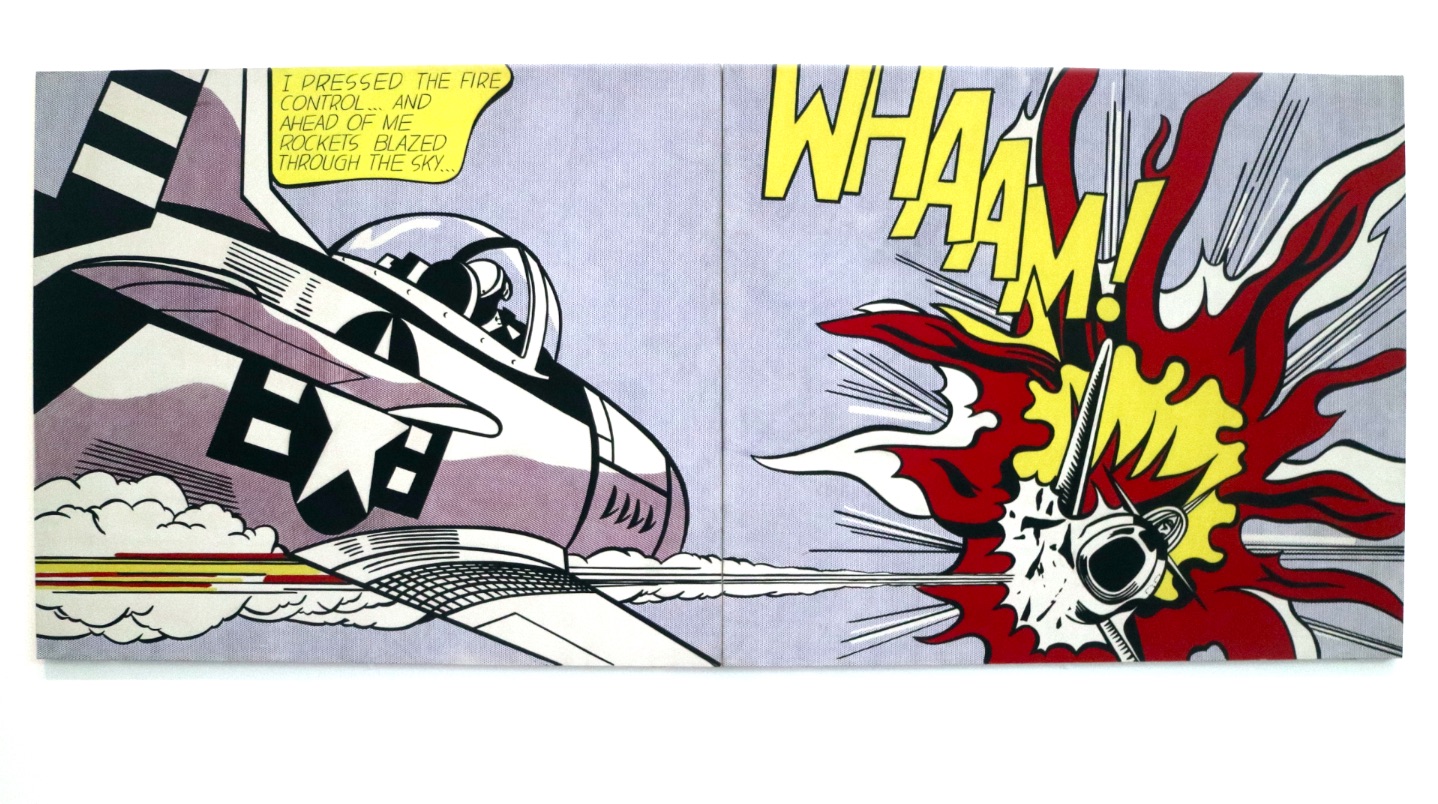
The Diverse and Influential World of Postmodern Art
Explore the rebellion of postmodern art: a world where norms are defied, boundaries blurred, and diverse cultures & narratives interweave boldly.

Introduction to Postmodern Art
Postmodern art emerged in the mid-20th century as a movement that replaced modernism. It encompasses a diverse range of art forms and styles, including Pop Art, Conceptual Art, Neo-Expressionism, Feminist Art, and Young British Artists. Postmodern art can be defined as a form of expression characterized by criticism, skepticism, and irony, rejecting modernism’s belief in progress and questioning the existence of an objectively comprehensible reality.
Postmodern art emerged as a response to the perceived limitations and rigidity of modernism. Modernism, which dominated the art world in the early 20th century, valued progress, rationality, and the pursuit of universal truths. However, postmodern artists began to question these ideals, challenging the notion that there is a single objective reality or a universal definition of art. Instead, they embraced subjectivity, ambiguity, and multiple perspectives.
One example of postmodern art is the work of Barbara Kruger. Kruger is known for her provocative and politically charged artworks that combine text and images. Her works often critique consumerism, gender roles, and societal norms. In her piece “Untitled (Your Body is a Battleground),” Kruger uses bold text and a powerful image to address issues of women’s rights and reproductive freedom. This artwork exemplifies the postmodern practice of appropriating existing images and using text to challenge established narratives.
Definition and Origins of Postmodern Art
Postmodern art emerged as a rejection of the traditional values of modernism and a desire to challenge and contradict established norms. It embraced experimentation with new media and art forms, leading to the development of various movements within postmodernism, such as pop art, word art, performance art, and installation art. Postmodern art is characterized by bricolage, prominent text, collage, appropriation, and performance art. It is also influenced by technology and often incorporates elements of low culture.
The origins of postmodern art can be traced back to the disillusionment with modernism’s ideals of progress and universal truths. Artists felt that modernism’s emphasis on rationality and the pursuit of objective reality limited their creative freedom. As a result, they sought to challenge and contradict the established norms through their art. The Neo-Dada style in the 1950s was considered a precursor to postmodern art, as it rejected traditional artistic conventions and embraced the use of everyday objects and found materials.
One notable characteristic of postmodern art is bricolage, which involves the combination of different materials and objects to create a new work of art. Artists use bricolage to challenge the boundaries of traditional art forms and create unexpected juxtapositions. An example of bricolage in postmodern art is the work of Joseph Cornell. Cornell created boxes filled with found objects, photographs, and other ephemera. His assemblages combine elements from different sources to create poetic and dreamlike compositions.
Key Characteristics and Themes of Postmodern Art
Postmodern art is characterized by its use of bricolage, prominent text, collage, appropriation, and performance art. These techniques and styles allow artists to create works that challenge traditional forms of representation and question established norms. Postmodern art often explores fragmented identity, critiques societal norms, and addresses issues of feminism. Iconic examples of postmodern artworks include Andy Warhol’s Marilyn Diptych, Roy Lichtenstein’s Whaam!, and Cindy Sherman’s Untitled Film Still #21.
The use of prominent text is a significant characteristic of postmodern art. Artists incorporate text into their artworks to convey messages, challenge meanings, and question established narratives. One example is the work of Jenny Holzer, who is known for her use of text in public spaces. Holzer’s LED displays feature thought-provoking statements and aphorisms that address themes of power, gender, and politics. Through her use of text, Holzer challenges the viewer’s perception of public spaces and prompts critical thinking.
Postmodern art often explores themes that critique societal norms and challenge established power structures. Feminism is one of the prominent themes addressed by postmodern artists. Feminist artists, such as Judy Chicago, explore issues of gender, sexuality, and the female experience. Chicago’s “The Dinner Party” is a notable example of postmodern feminist art. The installation features a triangular table with place settings for 39 historical and mythical women. Each place setting is intricately designed to represent the individual woman’s story and challenge traditional notions of women’s roles in history.
Influential Postmodern Artists and Their Works
Several artists have made significant contributions to the postmodern art movement. Andy Warhol, known for his iconic pop art, challenged traditional notions of art and consumer culture. Barbara Kruger used text and images to critique societal norms and gender roles. Roy Lichtenstein’s comic book-inspired artworks questioned the boundaries between high and low culture. Cindy Sherman’s photography explored themes of identity, gender, and representation. Other influential postmodern artists include Joseph Kosuth, Carolee Schneemann, Gilbert & George, Guerilla Girls, and Damien Hirst.
Damien Hirst, known for his controversial artworks, explores themes of life, death, and the fragility of existence. One of his most famous works, “The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living,” features a preserved shark suspended in a tank of formaldehyde. This artwork challenges traditional notions of beauty and raises questions about mortality and the nature of art. Hirst’s work is emblematic of the postmodern practice of pushing boundaries and challenging viewers’ perceptions.
Another influential postmodern artist is Joseph Kosuth, a pioneer of conceptual art. Kosuth’s works often consist of neon signs with text that explores language, meaning, and the nature of art itself. His piece “One and Three Chairs” is a classicOrigin: The term "Renaissance" was deeply influenced by the ... More example of postmodern conceptual art. The artwork consists of a chair, a photograph of the chair, and a dictionary definition of the word “chair.” Through this piece, Kosuth questions the relationship between objects, their representations, and the role of language in shaping our understanding of reality.
Techniques and Mediums Used in Postmodern Art
Postmodern art employs various techniques and mediums to convey its messages. Collage, appropriation, and performance art are commonly used in postmodern artworks. Artists often combine different materials and images to create layered and complex compositions. Additionally, postmodern art embraces new media and experimental forms, incorporating technology and multimedia elements.
Collage is a technique frequently used in postmodern art, allowing artists to create visual narratives by combining disparate elements. An example of collage in postmodern art is the work of Romare Bearden. Bearden’s collages often depict scenes of everyday life, combining fragments of photographs, magazine cutouts, and painted elements. Through his collages, Bearden explores themes of African American identity, history, and culture, challenging traditional narratives of representation.
Performance art is another technique used in postmodern art to create interactive and ephemeral experiences. Marina Abramović is a prominent artist known for her transformative and often provocative performances. In her piece “The Artist is Present,” Abramović sat silently in the Museum of ModernDefinition: Modernità encompasses the historical period tha... More Art for 736 hours while visitors were invited to sit across from her. This performance challenged the boundaries between the artist and the audience, exploring themes of presence, vulnerability, and human connection.
Impact and Criticism of Postmodern Art
Postmodern art has had a significant impact on the art world and has influenced subsequent artistic movements. It challenged traditional notions of authority and expertise, democratizing the art world and questioning established hierarchies. However, postmodern art has also faced criticism, with some accusing it of lacking coherence and meaninglessness. Nonetheless, it remains an important and influential movement in the history of art.
The impact of postmodern art extends beyond the art world. Its influence can be seen in other fields, such as architecture, literature, and film. Postmodern architecture, for example, rejects the modernist principles of simplicity and functionality. Instead, it embraces historical references, decorative elements, and a playful use of forms and materials. Postmodern buildings challenge the traditional notions of what a building should look like and create a dialogue with the surrounding urban environment.
Critics of postmodern art argue that its emphasis on subjectivity and multiple perspectives can lead to a lack of coherence and meaning. They claim that the rejection of universal truths and the focus on irony and skepticism undermine the artistic value of postmodern artworks. However, proponents of postmodernism argue that its exploration of diverse perspectives and its challenge to established norms create a more inclusive and democratic art world.
Postmodern Art’s Reflection of Disillusionment
Postmodern art reflects a sense of disillusionment with art, culture, and society. It discredits authority and expertise, embracing a belief that all types of art are valid. Postmodernism also encourages the inclusion of art from minority and feminist artists, promoting diversity and inclusivity.
Postmodern artists often express their disillusionment with the traditional art world by challenging established norms and rejecting the authority of experts. They question the idea that there is a single “correct” way to create or appreciate art. Instead, they celebrate the diversity of artistic expressions and challenge the notion that art should adhere to fixed criteria. Postmodern art embraces a belief that everyone’s perspective is valid and that art can be found in unexpected places.
Postmodern art also reflects a desire to include voices that have been historically marginalized. Feminist and minority artists have played a significant role in postmodernism, using their art to challenge patriarchal structures and promote inclusivity. Through their artworks, they address issues of gender, race, sexuality, and social justice, contributing to a more diverse and inclusive art world.
Postmodern Art as a Reaction against Modernism
Postmodern art emerged as a reaction against the mindset of modernism in the post-war era. The Neo-Dada style, which preceded postmodern art, challenged traditional values and paved the way for the development of postmodernism. Artists sought to challenge and contradict the established norms of modernism, embracing a more fragmented and diverse approach to art.
Modernism, with its emphasis on progress and universal truths, was seen by postmodern artists as restrictive and exclusionary. They rejected the notion that there is a single objective reality or a universal definition of art. Instead, postmodern artists embraced subjectivity, multiple perspectives, and a more inclusive approach to art-making. They sought to challenge the established norms and question the authority of modernist ideals.
One artist who exemplifies the reaction against modernism is Jasper Johns. Johns, a key figure in the Neo-Dada movement, created artworks that challenged the notions of originality and artistic expression. His iconic flag paintings, such as “Flag” and “Three Flags,” incorporate everyday symbols and objects, blurring the line between art and everyday life. By using familiar imagery, Johns questioned the idea of the artist as a unique and original genius.
Postmodern Art’s Addressing of Feminism and Elitism
Postmodern art addresses issues of feminism and challenges the elitism within the art world. Feminist artists have played a significant role in postmodernism, using their art to critique patriarchal structures and promote inclusivity. Through their works, they challenge traditional gender roles and highlight the experiences of women.
Feminist artists have used postmodern art as a platform to address gender inequality and challenge societal norms. They explore the representation of women in art and challenge traditional notions of beauty and femininity. Cindy Sherman, for example, uses photography to explore themes of identity and representation. In her series “Untitled Film Stills,” she presents herself in various roles, challenging the stereotypical portrayals of women in cinema and popular culture.
Postmodern art also seeks to challenge the elitism within the art world. It questions the notion that art should be confined to a select group of experts or institutions. Postmodern artists celebrate the democratization of art and believe that all types of art are valid. They challenge the hierarchical structure of the art world and open up opportunities for diverse voices and perspectives to be heard.
Postmodern Art’s Impact on Society and Culture
Postmodern art has had a broader impact on society and culture beyond the art world. It has influenced fields such as architecture, literature, and film. Postmodern art has shaped cultural movements and challenged societal norms, sparking discussions and raising awareness about various social issues.
The influence of postmodern art can be seen in architecture, where postmodern principles have been applied to create buildings that challenge traditional design conventions. Postmodern architecture rejects the modernist principles of simplicity and functionality. Instead, it embraces historical references, decorative elements, and a playful use of forms and materials. Postmodern buildings challenge the traditional notions of what a building should look like and create a dialogue with the surrounding urban environment.
In literature, postmodernism has influenced narrative techniques and storytelling. Writers such as Italo Calvino and Jorge Luis Borges employ fragmentation, intertextuality, and metafiction in their works. These techniques challenge traditional linear narratives and invite readers to question the nature of storytelling and the relationship between fiction and reality.
Postmodern art has also had an impact on film, with directors embracing postmodern principles in their storytelling. Filmmakers like Quentin Tarantino and the Coen brothers use intertextuality, nonlinear narratives, and self-referential elements in their films. These techniques challenge traditional storytelling conventions and engage audiences in a more active and critical viewing experience.
Conclusion
Postmodern art is a diverse and influential movement that emerged in the mid-20th century. It encompasses various art forms and styles, characterized by criticism, skepticism, and irony. Postmodern art challenges traditional forms of representation, explores fragmented identity, critiques societal norms, and addresses issues of feminism and elitism. It has had a significant impact on the art world and broader society, shaping cultural movements and challenging established norms. The legacy of postmodern art continues to inspire and influence artists today.